The TRANSIL AGP Binding Kit estimates the binding of drugs to human α1 acid glycoprotein (AGP/AAG). The assay kit measures the affinity constant (KD) of drugs to AGP and hence allows the calculation of AGP binding even under disease and physiological states that substantially alter the AGP content of human serum. In combination with our TRANSIL HSA Binding Kit it is possible to obtain accurate prediction of plasma protein binding in a highly controlled and reproducible assay environment. Internal quality controls provide easy assessment of recovery, experiment and data quality.
TRANSIL protein binding kits measure the dissociation constant (KD) of the test item in 6 intelligent replicates with varying protein concentration. This allows not only accurate KD determination, but also provides for detailed assay quality control, so that there is no need to perform additional experiments to assess recovery and concentration dependency. We also provide a spreadsheet for the data analysis and comprehensive quality control. The automatically calculates the test items’ dissociation constants and the fraction unbound according to this formula:

When results from TRANSIL HSA Binding and AGP Binding kits shall be combined, the spreadsheet calculates the unbound fraction according to the full binding equation:

The kit consists of ready-to-use 96 well microtiter plates. One plate can be used for measuring HSA binding of up to 12 compounds.
The assay protocol has only 5 steps:
- addition of drug candidate,
- mixing and incubation for up to 12 minutes,
- removal of beads by centrifugation,
- sampling of supernatant,
- quantification of drug candidate.
Plasma protein binding estimates obtained with TRANSIL kits are comparable to literature data and measurements obtained with dialysis (Figure 2). For most compounds even the measurements from the TRANSIL HSA Binding kit suffice for an accurate fraction unbound estimate. Only drugs with weak albumin binding and strong AGP binding, such as propranolol, exhibit strong change in the estimate of the unbound fraction when including the results from the TRANSIL AGP Binding kit (Figure 3).
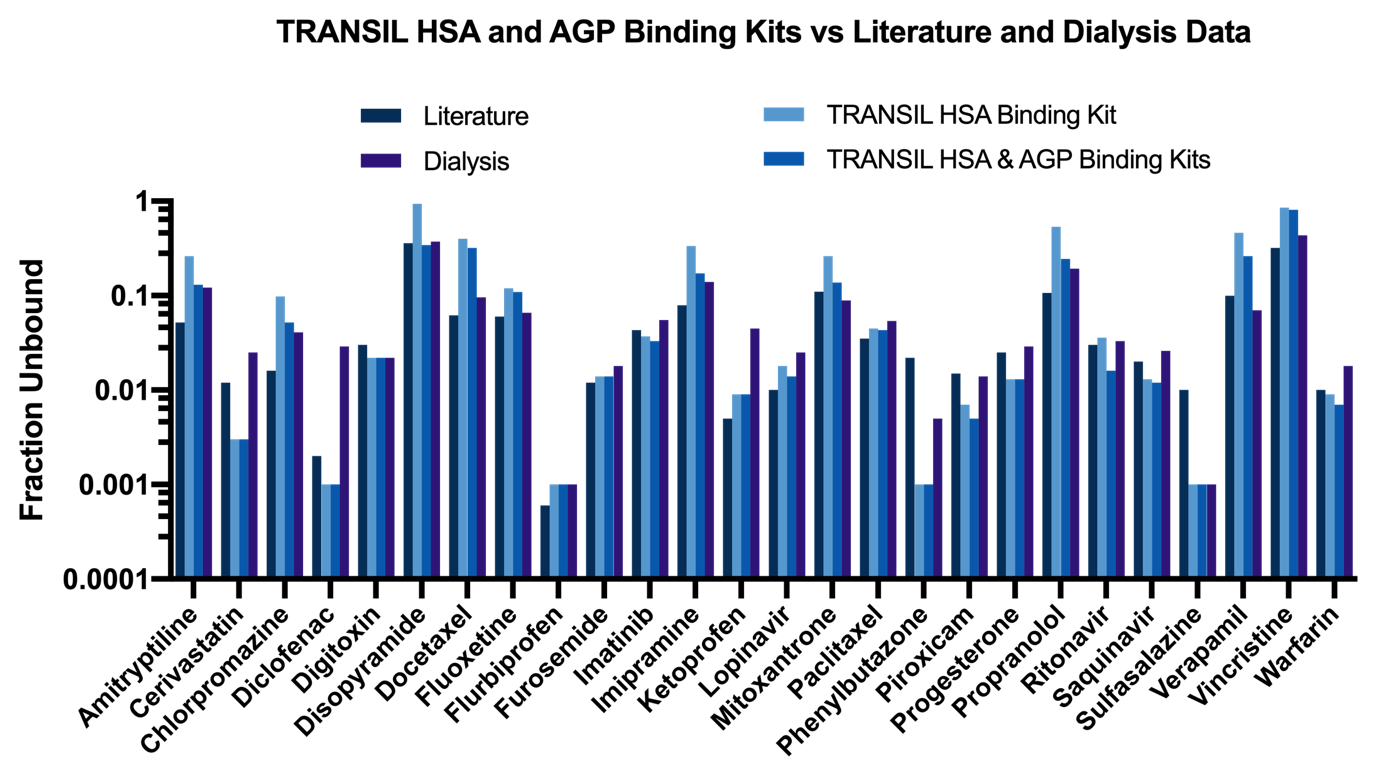 Figure 4: Comparison of plasma protein binding measurements obtained with the TRANSIL assay kits and dialysis as well as comparison with literature data (Goodman and Gilman 1996: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics).
Figure 4: Comparison of plasma protein binding measurements obtained with the TRANSIL assay kits and dialysis as well as comparison with literature data (Goodman and Gilman 1996: The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics).
The reason for the relatively rare contribution of AGP binding to the total fraction unbound is that AGP has a 30 times lower concentration in plasma than albumin (in fact, the ratio of HSA to AGP can vary between 1:15 and 1:85). Thus, when a compound binds strongly to albumin there is only a small net effect of additional binding to AGP due to the strong binding competition of albumin.